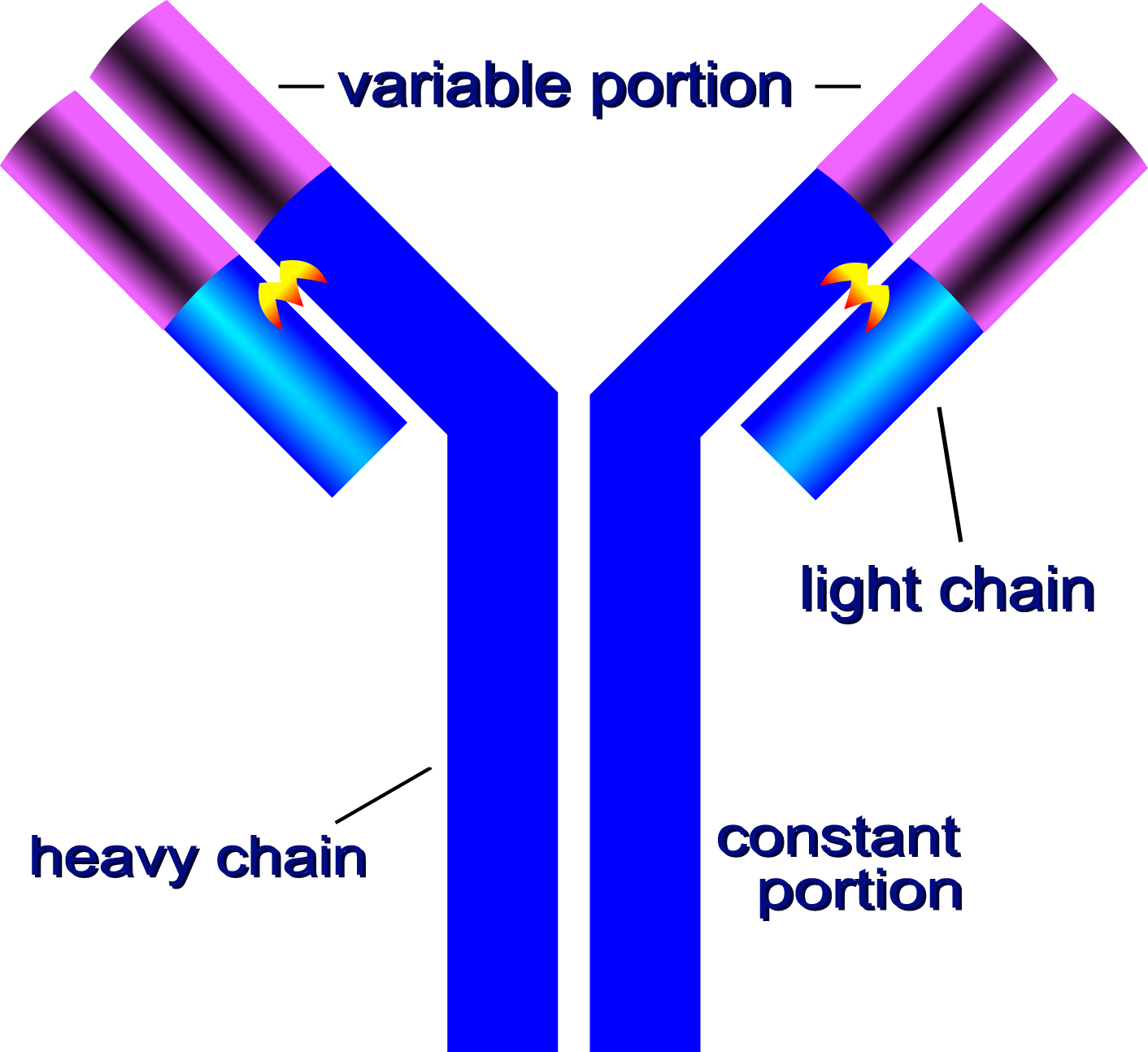
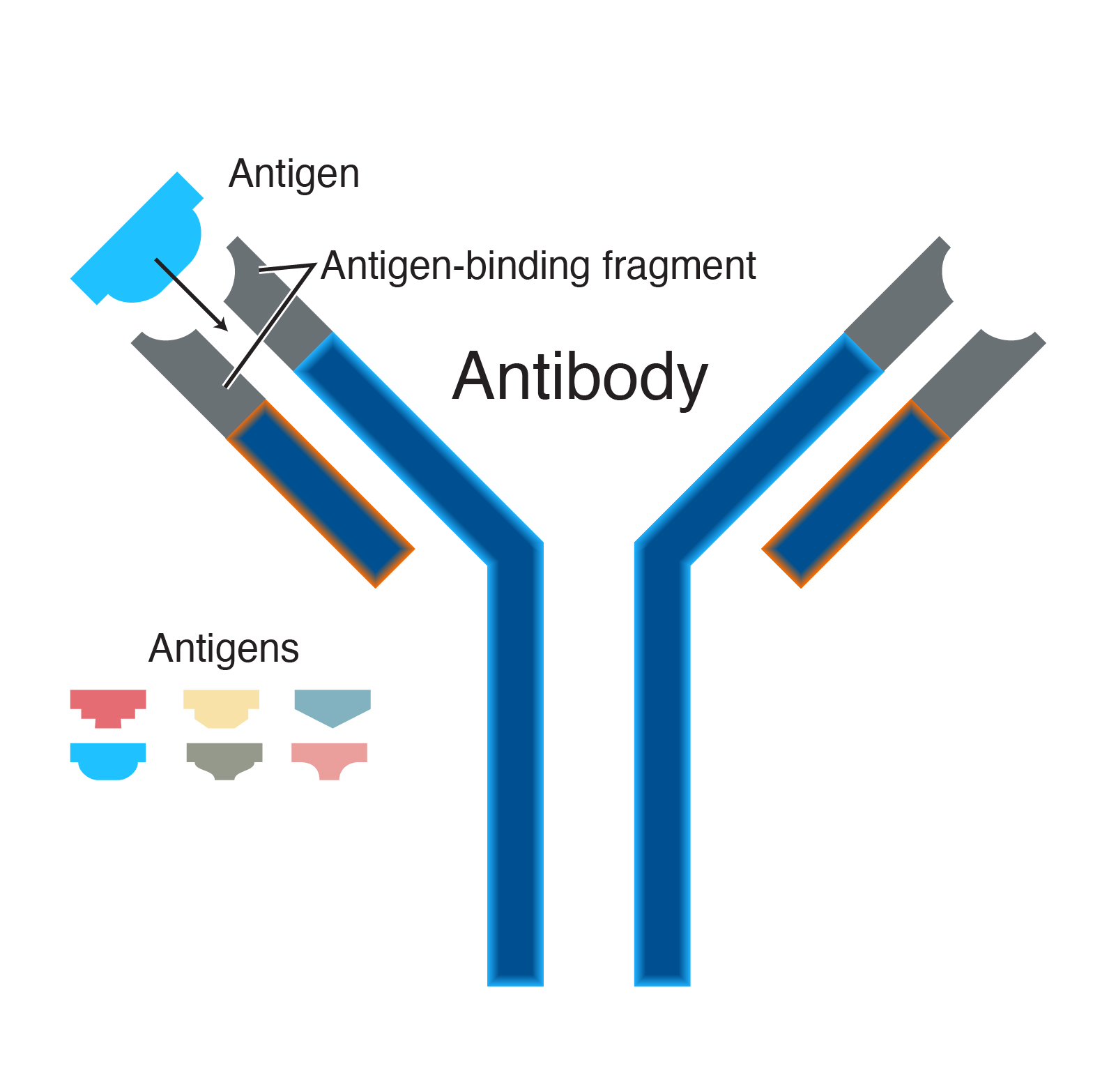
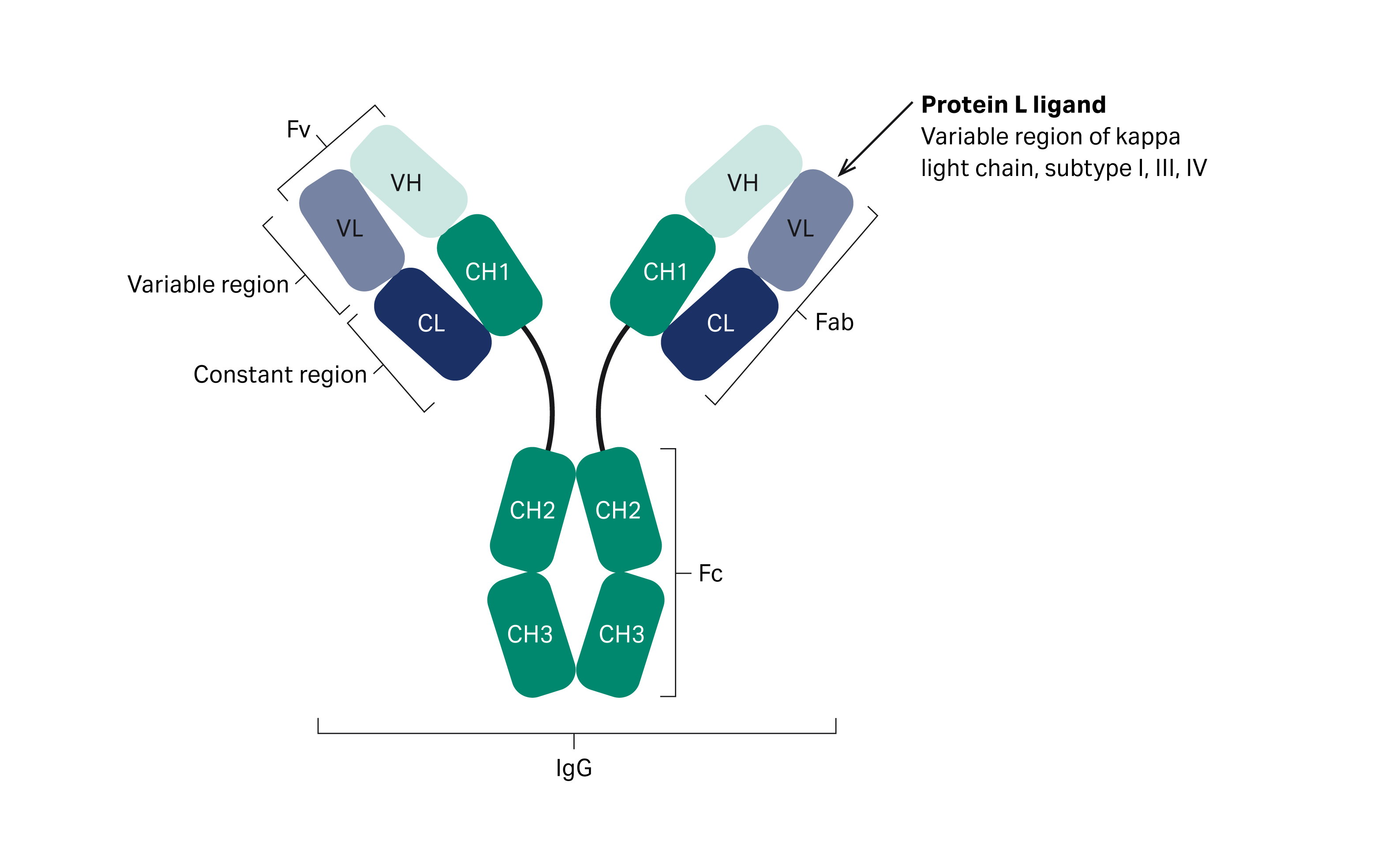
· antibody (ab) also know as immunoglobulin (ig) is the large y shaped protein produced by the body’s immune system when it detects harmful substances, called antigens … · each antibody has two light chains that are identical and only one of the two (lambda (λ) and kappa (κ)) light chains is present per antibody in mammals; Each type of antibody has a different amino … · the tip of the antibody consists of a hypervariable region that allows different antibody types to develop, making it possible to bind to a wide range of foreign substances that … Antibodies combine with specific antigens to generate an exclusive antibody-antigen complex. · an antibody can recognize and bind to an antigen in a specialized lock-and-key manner. · antibody, a protective protein produced by the immune system in response to the presence of a foreign substance, called an antigen. This binding triggers the body’s immune response and mobilizes other cells to fight … What do antibodies look like? Each antibody structure consists of two heavy chains and two light chains, which join to form a y-shaped molecule. Explore how antibody structure and isotype contribute to their function and use in research, and the application of antibody formats such as fab fragments and nanobodies. Antibodies recognize and latch onto … The basic principle of any immunoassay is that a specific antibody binds with its specific antigen, forming an exclusive antibody-antigen complex. Therefore either of … [3] antigen literally means antibody … Each individual antibody recognizes one or more specific antigens, [1][2] and antigens of virtually any size and chemical composition can be recognized. This chapter defines what an antigen is and … Learn about the nature of this bond and its use as a molecular tag for research.
Antibody Labeling Techniques: A Detailed Exploration
· antibody (ab) also know as immunoglobulin (ig) is the large y shaped protein produced by the body’s immune system when it detects harmful substances,...